ViT 살펴보기 | Vision Transformer
📺 Vision Transformer(ViT) 의 기본 원리와 구조, 수식을 정리했습니다.
KEYWORDS
Vision Transformer (ViT), ViT란, ViT Paper, ViT 모델, ViT 설명, ViT model, ViT 구조, ViT Architecture, ViT 논문리뷰, BEIT, CCT, CVT, DeiT, MobileViT, PvT, Swin Transformer, T2T-VIT
Original Paper Review | An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale
Overview
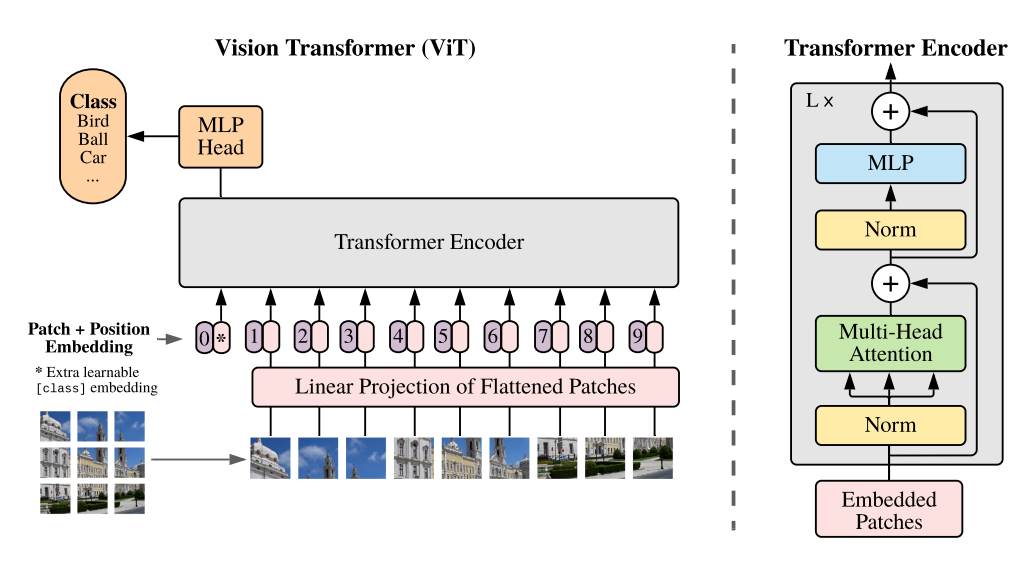
- Vision Transformer(ViT)는 Transformer 구조를 이미지 데이터 처리에 직접 적용한 모델입니다.
- Image Patch Sequence를 Input으로 하여 기존의 Transformer 구조를 거의 그대로 Vision Task에 활용합니다.
- CNN에 비해 Inductive Bias는 부족합니다.
➔ CNN이 가지는 Translation Equivariance 및 Locality 특성을 ViT는 갖추고 있진 않습니다.- 이는 ViT가 데이터 전체를 고려하여 Attention할 위치를 정하기 떄문입니다.
- 적은 데이터로 학습할 경우, Resnet50보다 성능이 더 떨어질 수 있습니다.
- Imagenet 21K (1400만 장), JFT-300M (3억 장) 으로 Pre-training, CIFAR-10 (6만 장) 으로 Transfer Learning
- Pretrained model의 크기는 약 300MB
Formulation
1. Input
(1) Image
- (C, H, W) = (Channel, Height, Width)
(2) Flatten
- \(P\): 패치 사이즈, \(N\): 이미지 당 패치의 개수
(3) Linear Projection
- \(D\): Latent Vector의 크기
(4) Insert the Class Token
- Class token은 BERT의 class token과 유사하며, Embedding patch들 앞에 학습 가능한 token을 추가합니다.
➔ Class token \(x_{cls}\) 은 Transformer의 여러 Encoder 층을 거쳐 \(z^0 _L\)로 변환됩니다.
➔ 최종적으로 이 값은 이미지에 대한 Representation Vector로 사용됩니다.
(5) Add the Positional Encoding
\[z_0= [x_{cls}; x^1_p E; x^2_p E; \cdots ; x^N_p] + E_{pos} \in \mathbb{R}^{(N+1)\times D} \quad \text{where} \quad E_{pos} \in \mathbb{R}^{(N+1)\times D}\]
2. Transformer Encoder
(1) Multi-Head Self Attention (MSA)
- Query(\(q\)), Key(\(k\)), Value(\(v\)) 간의 관계를 추출합니다.
- Self-Attention
- \(A\): Attention score matrix
- Attention score가 value(\(v\))와 곱해지면서 query(\(q\))와 key(\(k\))의 연관성이 value(\(v\))에 반영되어 그 중요도를 반영하게 됩니다.
- \(D^{\frac{1}{2}}_h\) 로 나누는 이유는 Softmax 값이 작은 Gradient를 가지는 것을 방지하기 위함입니다.
- Multi-head Self Attention
(2) Multi-Layer Perceptron (MLP)
- Pre-training ㅣ 1개의 Hidden layer 사용
- Fine-tuning ㅣ 1개의 Linear Layer 사용
(3) Encoder with L layers
\(L\): Layer 개수
Layer Normalization ➔ Multi-head Self Attention ➔ Skip Connection
Layer Normalization ➔ Multi-layer Perceptron ➔ Skip Connection
- \(\gamma, \beta\): 학습 가능한 파라미터
3. Output
- Class token \(z^0 _L\) 을 통해 최종 예측이 생성됩니다.
- \(C\): 클래스 개수
ViT Variants
BEIT (Bidirectional Encoder representation from Image Transformers)
Bao, Hangbo, et al. “Beit: Bert pre-training of image transformers.” arXiv preprint arXiv:2106.08254 (2021).
CCT (Compact Convolutional Transformers)
Hassani, Ali, et al. “Escaping the big data paradigm with compact transformers.” arXiv preprint arXiv:2104.05704 (2021).
CvT (Convolutional vision Transformer)
Wu, Haiping, et al. “Cvt: Introducing convolutions to vision transformers.” Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision. 2021.
DeiT (Data-efficient image Transformer)
Touvron, Hugo, et al. “Training data-efficient image transformers & distillation through attention.” International conference on machine learning. PMLR, 2021.
MobileViT
Mehta, Sachin, and Mohammad Rastegari. “Mobilevit: light-weight, general-purpose, and mobile-friendly vision transformer.” arXiv preprint arXiv:2110.02178 (2021).
PvT (Pyramid vision Transformer)
Wang, Wenhai, et al. “Pyramid vision transformer: A versatile backbone for dense prediction without convolutions.” Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision. 2021.
Swin Transformer
Liu, Ze, et al. “Swin transformer: Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows.” Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision. 2021.
T2T-VIT (Tokens-to-Token VIT)
Yuan, Li, et al. “Tokens-to-token vit: Training vision transformers from scratch on imagenet.” Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision. 2021.
ViT with Deformable Attention
Xia, Zhuofan, et al. “Vision transformer with deformable attention.” Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. 2022.
Reference
- Dosovitskiy, Alexey. “An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale.” arXiv preprint arXiv:2010.11929 (2020).